Jonathan Olmscheid, Chief Financial Officer
Very few headlines recently have not included tariffs or trade policies with the significance of large percentages being discussed by the US and other nations in retaliation. Tariffs and trade policies can have significant effects on various aspects of an economy, including interest rates, the stock market, commodity prices, and taxes.
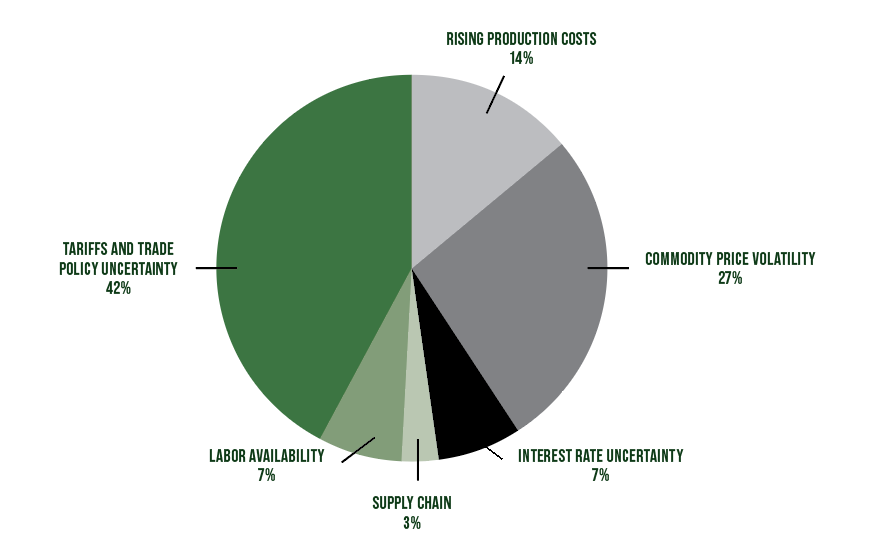
During a presentation in March at the National Society of Accountants for Co-ops (NSAC), NSAC surveyed participants on their biggest concern for cooperatives today. The answer was overwhelmingly tariffs and trade policy uncertainty, nearly double commodity price volatility.
Biggest concerns for coops
Below is how each of these areas might be impacted by tariffs and trade policies:
1. Interest Rates
- Short-Term Impact: Cost of imports can be increased, which may lead to higher overall inflation. Central banks may respond to this by adjusting interest rates. For instance, if inflation rises due to higher import prices, a central bank (like the Federal Reserve) might raise interest rates to curb inflation.
- Long-Term Impact: In the long run, if tariffs lead to slower economic growth or more trade imbalances, the central bank could lower interest rates to stimulate economic activity. However, higher tariffs may also result in less investment from foreign countries, potentially reducing demand for capital and affecting interest rate policies.
2. Stock Market
- Volatility: The stock market often reacts negatively to tariffs and trade policies due to the uncertainty they create. Companies that rely on global supply chains or exports may see their profit margins squeezed, leading to lower stock prices. For example, if tariffs are imposed on a key input, the cost of production for a company rises, and its stock may fall as a result.
- Sector-Specific Impact: Some sectors may benefit from tariffs, while others suffer. For example, domestic manufacturers might benefit from tariffs on imported goods, but tech companies that rely on global trade might face higher costs, negatively affecting their stock prices.
- Investor Sentiment: Uncertainty about the future of trade relationships can hurt investor sentiment, leading to more volatile markets. Investors may become cautious if they anticipate trade tensions to escalate further.
3. Commodity Prices
- Price Increases: Tariffs on imports can cause the prices of certain commodities (such as steel, aluminum, or oil) to rise, especially if these goods are heavily imported. Increased production costs may drive up the prices of finished goods, including consumer goods and manufacturing inputs.
- Global Supply Chains: If a country imposes tariffs on certain raw materials or goods, this can disrupt global supply chains and potentially lead to shortages or price spikes. For example, tariffs on Chinese imports may lead to higher prices for electronics or agricultural products, impacting global commodity prices.
- Impact on Global Trade: Commodities that are traded internationally can be affected by trade policies. If countries impose tariffs on agricultural products, the prices of these goods can fluctuate, impacting both producers and consumers globally.
4. Taxes
- Increased Tax Revenue: In some cases, tariffs can lead to higher tax revenue for governments, as they are essentially a form of tax on imports. This additional revenue might be used for domestic policy initiatives. For example, if a government imposes tariffs, the taxes collected could be used to fund infrastructure projects or social programs.
- Indirect Tax Effects: However, trade policies can also affect taxes in less direct ways. If tariffs lead to inflation or higher prices for consumers, there may be a push for increased taxation on businesses or individuals to counteract the negative economic effects. Additionally, the government may choose to reduce other taxes to offset the burden of tariffs on consumers.
- Tax Shifts: In some cases, governments might lower taxes elsewhere (e.g., corporate tax cuts) to offset the economic burden caused by tariffs, trying to keep businesses competitive despite higher import costs.
Regardless of how the tariffs and trade policies land and influence everything from interest rates to the stock market and commodity prices, your cooperative has a strong balance sheet to manage the resulting challenges and/or opportunities. Hopefully, if you were eligible, you all took advantage of the $10 billion in ad hoc disaster assistance to help mitigate increased input costs and falling commodity prices experienced in 2024. The Emergency Commodity Assistance Program was approved by Congress in December, the deadline to submit ECAP applications to FSA was April. 15, 2025.
